Positioning Ground Control Points (GCPs)
1. Description
This article presents the best practices to follow while installing and using GCP (Ground Control Points) hardware on the field, prior to flying a drone, in order to get the best possible experience and results while processing the data collected, with Aether.
There are two principles for the appropriate distribution of the GCP targets on the ground which is essential for the success of the operation.
First principle: The quantity of required GCP to be set on the ground depends on two factors :
- The site size to be surveyed
- The altitude you want to fly
Second principle: The visual quality of the GCPs remains imperative to keep accuracy at best throughout the project.
2. Best practices
Tip 1: Use a starred distribution - with one GCP every 300m
Targets will act as a traverse; one single target would not be as accurate as a network spread over the site. It is recommended to start from the site boundaries prior to adding GCPs inward.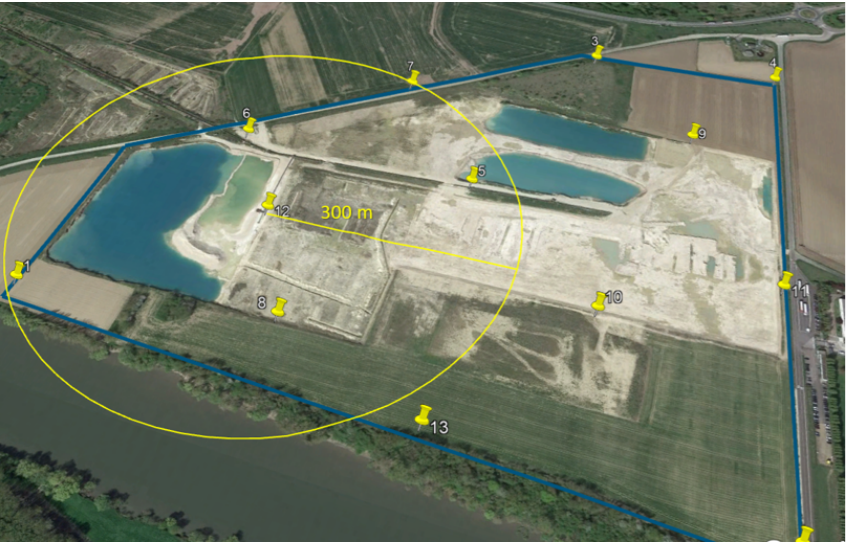
Tip 2: Take topography into account
Targets should be spread on high and low points. It is ideal to place GCP at both extremes so as to capture data in downs and maintain data accuracy all the way up.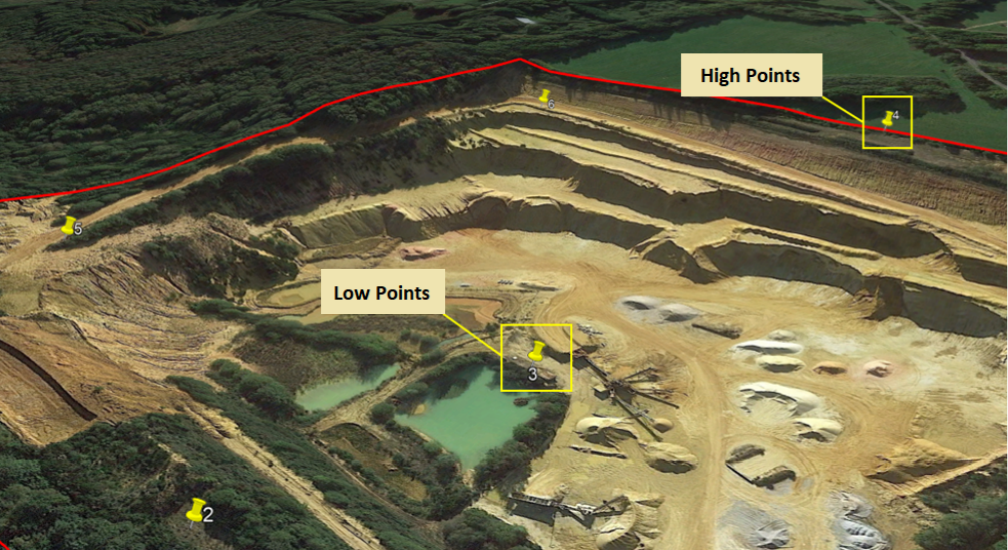
Tip 3a: In a quarry, pay special attention to the stockpiles area
Stockpiles area is usually a zone of potential higher uncertainty as a result of GCPs bad practices. The accuracy of Volume Calculations depends heavily on the steadiness of the targets during operation. It is highly recommended to increase the density of targets in such areas.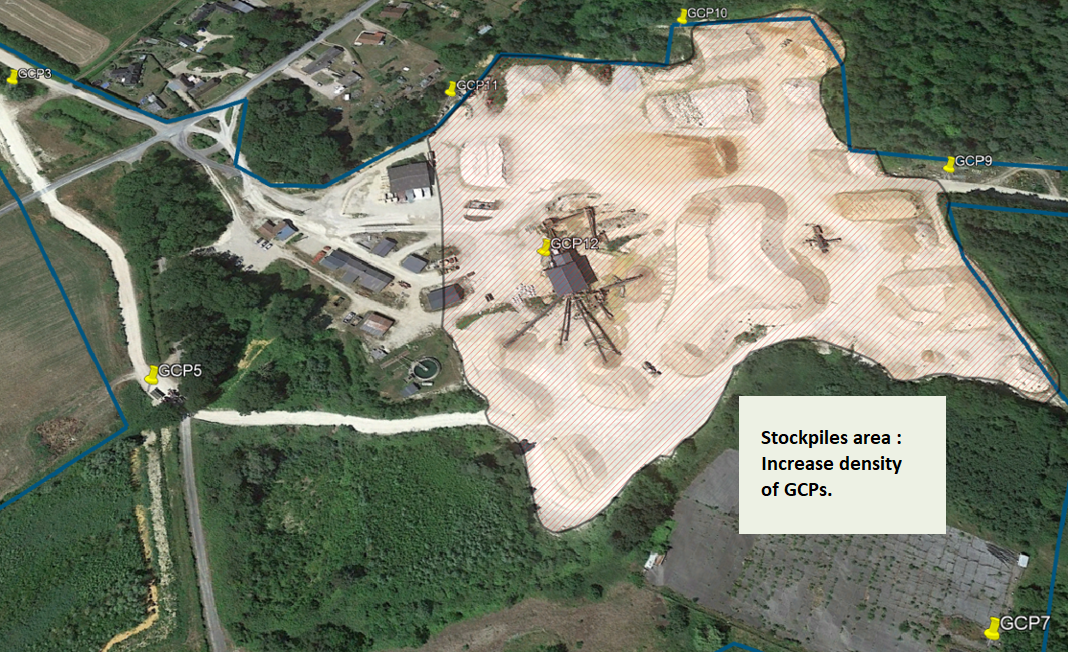 
Tip 3b: In an Agricultural field
Make sure that there is one GCP at each parcel border or corner
Tip 4: Keep your GCPs in place anytime
GCPs should not be moved during the operation. Once target positions have been measured, each displacement of a target would result in a risk of increased inaccuracy during data processing. It is recommended to brief all site stakeholders who could potentially interfere with the targets.
In case of accidental movement, we strongly advise you to inform us on our support portal so that provision shall be made to ignore the moved GCP, or to update the position in processing for the new one if it could be measured. We advise removing obsolete positions and reloading a file of the latest positions.
Tip 5: Keep your GCPs clean
Cleaning targets, especially in dusty areas is key to ensuring the best accuracy possible.
Tip 6: Use easily detectable GCPs - with a single central point
- We recommend using checkerboard-type GCPs to have an easily identifiable center
- Painted crosses or strips are not recommended since they do not provide a good level of precision
Tip 7: GCPs in the same CRS as the Project
This practice avoids converting geographical coordinates with the risk of introducing a potential bias.
Please consult the last part of the Coordinate Reference Systems article to view the Project CRS.
Tip 8: Track Vertical Reference System
Ensure to note and report in the file in which vertical system the GCPs positions have been measured.
Tip 9: File name
Adopt a standard file naming such as :
- GCP-YearMonthDay-Project-EPSG_Number-Vertical_CRS.csv
- Example: GCP-20191030-Paris-EPSG_3944-RAF09.csv


